Advanced Capabilities
Multimodal Reasoning Tasks
All tasks are “Vision-Language Tasks,” meaning that it is insufficient to
obtain the correct answer by relying solely on either the text or image.
This approach effectively avoids single-modality bias. Tasks including the
following four categories:
Basic logical reasoning: Tasks included deduction, induction, and
abduction, adapted from classic frameworks in cognitive psychology and
formal logic. Each problem was restructured into an image-text format.
Common-sense reasoning: Tasks involved scenarios based on everyday
life, combined with images, to test whether a model can ground its reasoning
in both visual context and text.
Discipline-specific reasoning: Task included single- or
multiple-choice problems to test specific discipline knowledge and
application. Questions were sourced from recent high school and university
entrance examinations in China and from the widely used multi-discipline
multimodal question dataset MMMU2.
Social phenomena reasoning: Tasks included customized multimodal
tasks built around real-world contexts like environmental protection, public
behavior, social responsibility, moral judgment, and ethical conflict.
Unlike traditional knowledge-based Q&A, these tasks emphasized contextual
understanding, identifying ethical dilemmas, and making judgments after
integrating multiple modalities. This examined a model’s ability to extend
logical inference to complex, real-world scenarios.
| Category | Question |
|---|---|
| Basic Logical Reasoning |
Riders must be over 1.5 meters tall to get on the
roller coaster. Does the person in the photo meet
the requirement?
A. Yes B. No 
|
| Common-sense Reasoning |
Looking at the picture, how many actual cats can you
spot?

|
| Discipline-specific Reasoning |
As shown in the figure, the smooth horizontal track
AB is connected to a smooth semicircular track BC in
a vertical plane at point B. A small block
compresses a light spring at point A, and is then
released from rest. After leaving the spring, the
block enters the semicircular track and just manages
to reach the highest point C.
Which of the following statements is correct? A. The net force on the block at point C is zero. B. The block's speed at point C is zero. C. The block's centripetal acceleration at point C is equal to the acceleration due to gravity. D. The elastic potential energy stored in the spring at point A is equal to the kinetic energy of the block at point C. 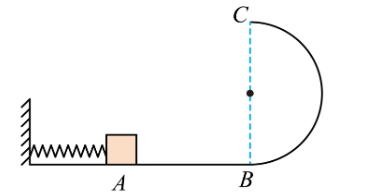
|
| Social Phenomena Reasoning |
Briefly explain the underlying message of the cartoon.
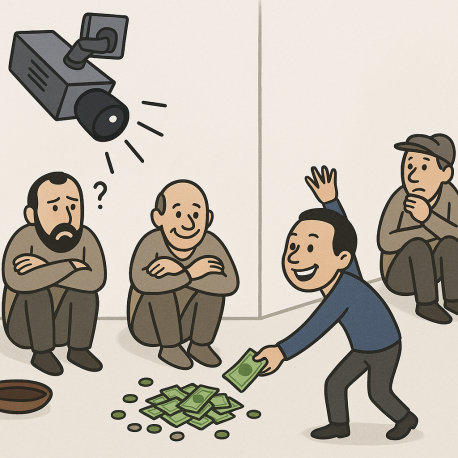

|
Table 1 Multimodal Reasoning Example Questions
Olympiad-level Reasoning Tasks
The Olympiad-level reasoning question set was drawn from recent International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO), Chinese Mathematical Olympiad (CMO), and other prestigious competitions (examples in Table 2). These problems are far more challenging than standard high school or college entrance exam questions. They typically involve complex logical structures, multi-step reasoning, and creative problem-solving. These tasks assessed whether models can go beyond rote memorization to demonstrate real reasoning capability under pressure.
| Category | Question |
|---|---|
| Olympiad-level Reasoning |

|
Table 2 Olympiad Question Example
